Radon gas represents one of the most significant yet overlooked health hazards facing Georgia homeowners today. As the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States—responsible for approximately 21,000 deaths annually—radon exposure demands serious attention from every property owner in the Peach State.
This comprehensive guide provides an authoritative examination of radon levels across Georgia, drawing on EPA data, geological research, and over 15 years of professional radon testing experience throughout Metro Atlanta and beyond. Whether you're a homeowner, real estate professional, or concerned resident, this resource will equip you with the knowledge necessary to understand and address radon risks in your community.
1. What Is Radon and Why Should Georgians Care?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas produced by the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and groundwater. Colorless, odorless, and tasteless, radon is virtually undetectable without specialized testing equipment. When radon seeps into enclosed spaces like homes and buildings, it can accumulate to dangerous concentrations.

Radon enters homes through foundation cracks, sump pumps, and other openings in direct contact with soil
The Radon Decay Process
Understanding how radon forms helps explain why Georgia experiences elevated levels:
- 1.Uranium-238 naturally present in Georgia's granite bedrock begins radioactive decay
- 2.Radium-226 forms as an intermediate decay product
- 3.Radon-222 gas is released, which has a half-life of 3.8 days
- 4.Radon daughters (polonium, lead, bismuth) are produced and attach to dust particles
- 5.These particles are inhaled and deposit in lung tissue, causing cellular damage
Why Georgia Faces Elevated Risk
Several factors combine to make Georgia a state of particular concern for radon exposure:
- ✓Granite-Rich Geology: The Piedmont region contains extensive granite formations with high uranium content
- ✓Climate Conditions: Temperature differentials create stack effect, drawing soil gases into homes
- ✓Construction Practices: Many Georgia homes feature basements and crawl spaces in contact with soil
- ✓Low Awareness: Compared to northern states, fewer Georgia homeowners test for radon
2. Understanding Georgia's EPA Radon Zones
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has classified every county in the United States into one of three radon zones based on predicted average indoor radon screening levels. Understanding these classifications is essential for assessing risk in your area.
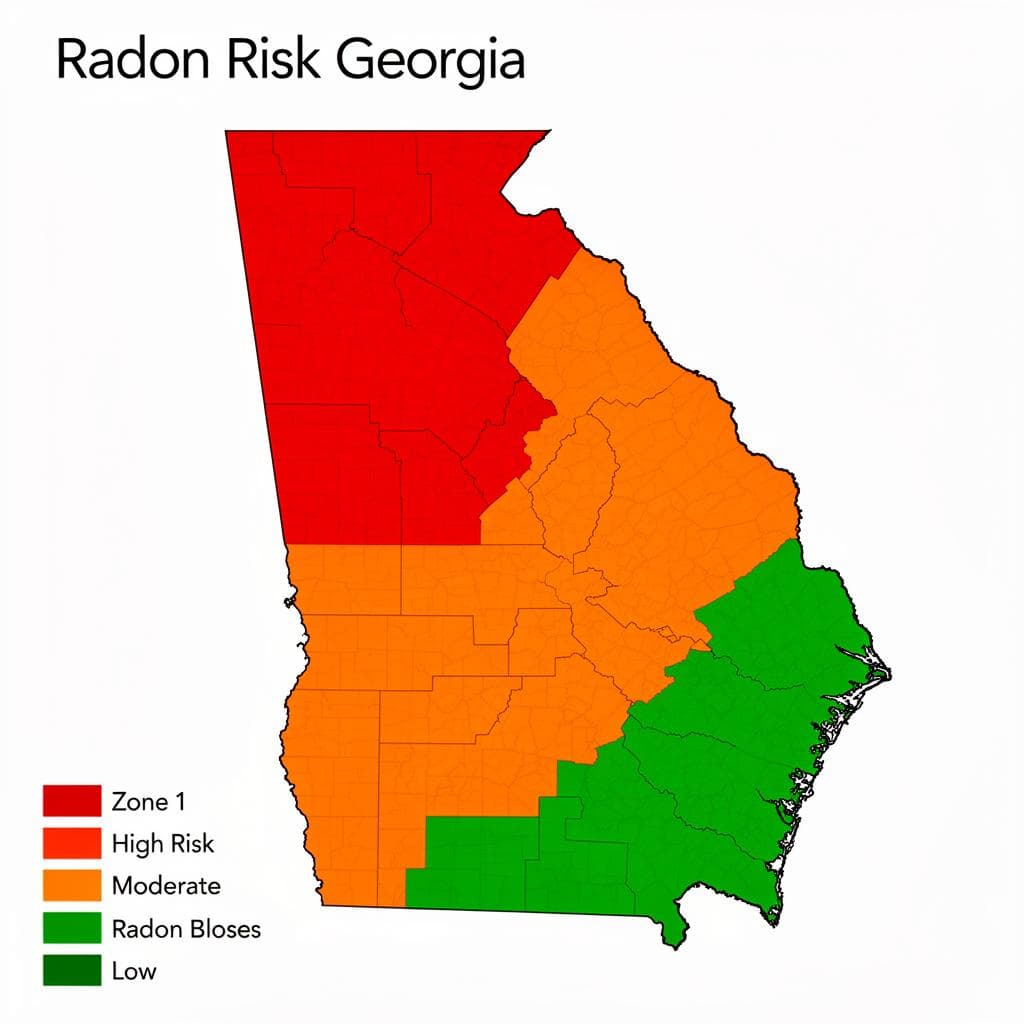
EPA Radon Zone Map of Georgia: Red indicates Zone 1 (highest risk), Orange indicates Zone 2 (moderate risk), Green indicates Zone 3 (lower risk)
EPA Zone Classifications Explained
Zone 1 (Highest Risk)
Predicted average indoor levels >4 pCi/L
Immediate testing and mitigation recommended
Zone 2 (Moderate Risk)
Predicted average indoor levels 2-4 pCi/L
Testing strongly recommended
Zone 3 (Lower Risk)
Predicted average indoor levels <2 pCi/L
Testing still recommended
⚠️ Critical Understanding
Zone designations are based on average predictions. Individual homes can have radon levels significantly higher or lower than zone averages. The only way to know your home's actual radon level is through professional testing. High-radon homes exist in every zone, and low-radon homes can be found in Zone 1 areas.
3. County-by-County Radon Analysis: Metro Atlanta Focus
Metro Atlanta encompasses diverse geological conditions that create variable radon risks across the region. Below is our detailed analysis of key counties based on EPA data and our extensive testing experience.
Zone 1 Counties (Highest Risk)
These Metro Atlanta counties have the highest predicted radon levels and should be prioritized for testing:
Gwinnett County
EPA Zone 1 | Population: 950,000+ | Average observed levels: 4.2-6.8 pCi/L
Gwinnett County's position on the Piedmont Plateau creates significant radon risk. The county's granite-gneiss bedrock, combined with rapid suburban development, makes radon testing essential for homes in Lawrenceville, Buford, Snellville, Duluth, Suwanee, Lilburn, and Norcross.
- •Highest concentration of Zone 1 testing failures in Metro Atlanta
- •Basement homes show 40% higher levels than slab foundations
- •Older neighborhoods (pre-1990) require immediate testing priority
Cobb County
EPA Zone 1 | Population: 760,000+ | Average observed levels: 3.8-5.5 pCi/L
Cobb County's diverse geology, including granite intrusions and metamorphic rock formations, creates variable but often elevated radon levels. Key areas of concern include Marietta, Kennesaw, Smyrna, Acworth, and Powder Springs.
- •Western Cobb shows highest concentrations due to mountain proximity
- •Historic districts with older foundations require special attention
- •Active soil depressurization is the most effective mitigation method
Cherokee County
EPA Zone 1 | Population: 270,000+ | Average observed levels: 4.5-7.2 pCi/L
Cherokee County consistently records some of the highest radon levels in Metro Atlanta due to its position at the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains. Woodstock, Canton, Holly Springs, and Ball Ground all show elevated readings. Nearby Cartersville in Bartow County also shows high radon levels.
- •Mountainous terrain creates high uranium concentration in bedrock
- •New construction should include radon-resistant building techniques
- •Annual testing recommended due to seasonal variations
Forsyth County
EPA Zone 1 | Population: 250,000+ | Average observed levels: 4.0-6.5 pCi/L
One of Georgia's fastest-growing counties, Forsyth's granite-rich geology means many new homes are built on high-radon soil. Cumming and newer developments require pre-construction radon prevention. Hall County to the north, including Gainesville, also shows elevated levels due to similar geology.
Hall County (Gainesville)
EPA Zone 1 | Population: 210,000+ | Average observed levels: 4.0-5.8 pCi/L
Hall County sits on granite-gneiss bedrock in the northern Piedmont, creating consistently elevated radon levels. Gainesville, the county seat, requires mandatory testing for all properties. Lake Lanier communities face particular risks due to the granite formations surrounding the lake.
Zone 2 Counties (Moderate Risk)
These counties have moderate predicted levels but still require testing:
DeKalb County
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 760,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.5-4.8 pCi/L
DeKalb County presents a mixed picture with significant variation across neighborhoods. Areas closer to Stone Mountain show elevated levels due to granite exposure, while southern portions tend to have lower readings. Key areas include Decatur, Dunwoody, and Brookhaven.
Fulton County (Atlanta)
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 1,050,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.0-4.5 pCi/L
Fulton County spans from the mountains in the north to flatter terrain in the south, creating variable radon risk. North Fulton cities like Alpharetta, Johns Creek, Roswell, and Sandy Springs show higher levels. Atlanta neighborhoods like Buckhead, Midtown, and Virginia-Highland require individual testing.
Henry County
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 240,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.2-3.8 pCi/L
South of Atlanta, Henry County shows moderate radon potential with some localized high-level areas. McDonough and Stockbridge warrant attention, particularly in newer developments with basement construction.
Fayette County
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 115,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.0-3.5 pCi/L
Fayette County, including Peachtree City and Fayetteville, shows moderate radon risk. The county's position at the edge of the Piedmont Plateau means testing is essential for accurate assessment.
Coweta County (Newnan)
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 155,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.5-4.2 pCi/L
Coweta County southwest of Atlanta shows moderate radon potential. Newnan, the county seat, has historic homes and newer developments that both require testing. The county's growing population makes radon awareness increasingly important.
Newton County (Covington)
EPA Zone 2 | Population: 115,000+ | Average observed levels: 2.2-3.8 pCi/L
Newton County east of Atlanta has moderate radon risk. Covington's historic downtown and surrounding residential areas should all be tested, especially older homes with basement or crawl space construction.
Zone 3 Counties (Lower Risk - Testing Still Recommended)
Clayton County
EPA Zone 3 | Population: 290,000+ | Average observed levels: 1.2-2.5 pCi/L
While Clayton County has lower predicted averages, individual homes can still exceed EPA action levels. Testing remains important, especially for homes with basements or crawl spaces in direct soil contact.
Douglas County
EPA Zone 3 | Population: 150,000+ | Average observed levels: 1.5-2.8 pCi/L
Douglas County west of Atlanta shows generally lower levels, but localized hotspots exist. Douglasville and surrounding areas should still conduct baseline testing.
Rockdale County
EPA Zone 3 | Population: 90,000+ | Average observed levels: 1.3-2.4 pCi/L
Rockdale County, including Conyers, has lower average levels but proximity to granite formations means some homes exceed EPA guidelines. Testing is recommended during real estate transactions.
4. Geological Factors Affecting Georgia Radon Levels
Georgia's diverse geology creates a complex radon landscape. Understanding these geological factors helps explain why radon levels vary dramatically across the state.
The Piedmont Plateau
The Piedmont region, stretching from the Fall Line to the Blue Ridge Mountains, contains the state's highest radon concentrations. This area is characterized by:
- •Granite Intrusions: Large granite formations, including Stone Mountain and numerous smaller outcrops, contain elevated uranium levels
- •Gneiss and Schist: Metamorphic rocks common throughout the Piedmont also harbor uranium-bearing minerals
- •Fractured Bedrock: Cracks and fissures in rock create pathways for radon to migrate toward the surface
- •Soil Permeability: Sandy and gravelly soils allow easy radon movement from bedrock to foundations
The Blue Ridge Mountains
North Georgia's mountainous terrain presents unique radon challenges. Ancient rock formations, some over one billion years old, contain significant uranium deposits. Counties like Cherokee, Forsyth, and Dawson regularly record the state's highest radon levels.
The Coastal Plain
South of the Fall Line, Georgia's Coastal Plain generally shows lower radon potential due to:
- ✓Younger sedimentary deposits with lower uranium content
- ✓Higher water tables that can block radon migration
- ✓Sandy soils that allow radon to dissipate before reaching foundations
However, localized phosphate deposits in south Georgia can create unexpected radon hotspots, reinforcing the importance of testing regardless of zone designation.
5. Health Risks of Radon Exposure
Understanding the health implications of radon exposure underscores the importance of testing and mitigation for Georgia homeowners.
Radon and Lung Cancer: The Statistics
- •Radon causes approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths annually in the United States
- •It is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers
- •Smokers exposed to high radon levels face up to 10 times greater risk than non-smokers
- •There is no safe level of radon exposure—risk increases with concentration and duration
How Radon Causes Cancer
When radon gas is inhaled, it decays into radioactive particles that lodge in lung tissue. These particles emit alpha radiation that damages DNA in surrounding cells. Over time, this cellular damage can lead to cancer development. The risk is cumulative—prolonged exposure to even moderate levels can be dangerous.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups face heightened risk from radon exposure:
- •Children: Higher respiratory rates and developing lungs increase vulnerability
- •Elderly residents: Cumulative lifetime exposure and reduced cellular repair capacity
- •Current and former smokers: Synergistic effect dramatically increases cancer risk
- •Pets: Dogs and cats are also susceptible to radon-induced lung cancer
6. Professional Radon Testing Protocols
Accurate radon testing requires proper protocols to ensure reliable results. Here's what Georgia homeowners should know about professional radon testing.
Types of Radon Tests
Short-Term Tests (2-7 days)
- • Continuous radon monitors (CRM)
- • Charcoal canisters
- • Electret ion chambers
- • Ideal for real estate transactions
- • Provides snapshot of current levels
Long-Term Tests (90+ days)
- • Alpha track detectors
- • Electret ion chambers
- • Provides annual average estimate
- • Accounts for seasonal variation
- • More accurate for health risk assessment
EPA Testing Guidelines
- 1.Test in the lowest livable area of the home (basement or ground floor)
- 2.Keep windows and doors closed except for normal entry/exit
- 3.Place test device away from drafts, high heat, and humidity
- 4.Maintain closed-house conditions 12 hours before and during testing
- 5.Do not disturb the test device during the testing period
Understanding Your Results
<2 pCi/L
Low risk - no action required
Retest every 2-5 years
2-4 pCi/L
Consider mitigation
EPA recommends action
>4 pCi/L
Mitigation recommended
EPA action level exceeded
7. Radon Mitigation Solutions for Georgia Homes
When testing reveals elevated radon levels, professional mitigation can reduce concentrations by up to 99%. Here are the primary mitigation methods used in Georgia homes.
Sub-Slab Depressurization (Most Common)
Sub-slab depressurization is the most effective and widely used mitigation technique for Georgia homes. The system works by:
- ✓Creating suction beneath the foundation slab
- ✓Drawing radon-laden air from the soil before it enters the home
- ✓Venting the gas safely above the roofline
- ✓Operating continuously with minimal energy use
Sub-Membrane Depressurization (Crawl Spaces)
For Georgia homes with crawl spaces, sub-membrane depressurization involves installing a heavy-duty vapor barrier over exposed soil and creating negative pressure beneath it to capture and vent radon gas.
Mitigation System Components
- •Suction Point: Core drilled through the slab to access sub-slab soil
- •PVC Piping: 3-4 inch Schedule 40 pipe routes from suction point to exterior
- •Radon Fan: Specialized inline fan creates continuous negative pressure
- •Discharge Point: Pipe extends above roofline for safe gas release
- •Manometer: Visual indicator confirms system is operating
System Maintenance
Radon mitigation systems require minimal but important maintenance. Regular inspection and repair ensures continued effectiveness. Key maintenance includes:
- •Monthly manometer checks to confirm fan operation
- •Fan replacement every 7-10 years (average lifespan)
- •Annual retesting to verify continued effectiveness
- •Inspection of pipe connections and seals
8. Radon and Georgia Real Estate Transactions
Radon testing has become an essential component of Georgia real estate transactions. Real estate professionals and homebuyers should understand the implications.
Georgia Disclosure Requirements
While Georgia does not mandate radon testing before sale, sellers are required to disclose known radon issues. The Georgia Seller's Property Disclosure Statement includes questions about radon testing history and any mitigation systems installed.
Best Practices for Buyers
- ✓Include radon testing as part of your home inspection contingency
- ✓Request testing results within the due diligence period
- ✓If levels exceed 4 pCi/L, negotiate mitigation as condition of sale
- ✓Verify any existing mitigation system is functional
- ✓Request post-mitigation test results for homes with systems
For Sellers
Proactive sellers may benefit from pre-listing radon testing. If levels are low, this provides a selling point. If elevated, mitigation before listing can prevent deal complications and demonstrate responsible homeownership.
Mitigation System Value
A properly installed and documented radon mitigation system can be a positive feature for prospective buyers, demonstrating that the home has been tested and protected. Systems typically cost $800-$2,500 depending on home construction and complexity.
9. Action Steps to Protect Your Family
Protecting your family from radon exposure requires a proactive approach. Here's your action plan:
1Schedule Professional Testing
Contact a certified radon testing professional to conduct an accurate assessment of your home's radon levels. EraseRadon provides EPA-protocol testing with 48-hour results.
2Understand Your Results
Review your test results with a radon professional who can explain the implications and recommend appropriate next steps based on your specific situation and home construction.
3Mitigate If Necessary
If levels exceed 4 pCi/L (or even 2 pCi/L for maximum protection), invest in professional mitigation. Modern systems are effective, quiet, and energy-efficient.
4Maintain and Retest
After mitigation, retest to confirm effectiveness. Continue testing every 2-5 years, after major renovations, or if you notice changes in your home's foundation or ventilation.
5Spread Awareness
Share information about radon risks with neighbors, family, and friends. Many Georgia homeowners remain unaware of this invisible threat. Your advocacy could save lives.
Ready to Protect Your Georgia Home?
Don't wait to find out if your home has elevated radon levels. With testing that takes just 48 hours and mitigation that can reduce levels by up to 99%, protecting your family has never been more accessible.
Contact EraseRadon today to schedule your professional radon test and take the first step toward a safer home.
About the Author
This guide was prepared by the EraseRadon Atlanta team, certified radon testing and mitigation professionals with over 15 years of experience protecting Georgia families from radon exposure. Our team has tested thousands of homes across Metro Atlanta and installed mitigation systems in every type of Georgia home construction.



